Archive
MPLS Layer 3 VPNs Troubleshooting
I would like to dedicate this post to MPLS L3 VPNs troubleshooting and more particularly using the Traceroute command. It can be sometimes difficult to find out where is the issue when testing connectivity between sites attaches to a MPLS VPN backbone. I will explain the behavior of Traceroute in MPLS VPN environment which is quite different than in “classical” IP environment. Finally I will talk about the MPLS LSP Ping feature and how to use it to detect break in MPLS LSP.
Topology:
I am using almost the same topology as the one used in this post: Basic MPLS. I have just added a P router.
Platform/IOS:
Cisco 2691/12.4(15)T11 Adv IP services
First of all if you want to get a basic understanding of MPLS and MPLS Layer 3 VPNs I suggest to read my previous posts: Basic MPLS and MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
The following is already configured:
- MP-iBGP between R2 and R5
- EBGP between R2 and R1, R5 and R6
- OSPF area 0 between R2,R3,R4,R5
- LDP between R2,R3,R4,R5
- R3 and R4 are P routers and R2 and R5 are PE routers
- R1 is representing the CE device at Site A announcing its loopback address 1.1.1.1/32
- R2 is representing the CE device at Site B announcing its loopback address 6.6.6.6/32
In this troubleshooting scenario we want to focus on the loopbacks reachability between Site A and Site B.
MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
This post is the continuation of the previous post I made on Basic MPLS. In this post, I will talk about the different steps in order to configure MPLS Layer 3 VPNs which include the PE-CE routing protocols configuration with RIP, EIGRP and OSPF. I will also talk about the different loop prevention rules used when using OSPF as a PE-CE routing protocol. Finally I will conclude this post by talking about OSPF Sham-link.
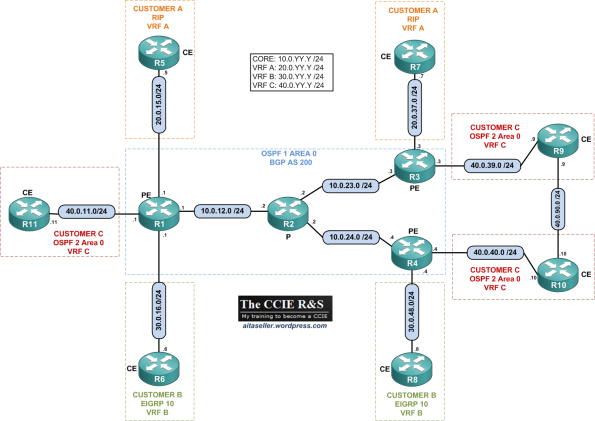
In this topic, I will use the following topology:
Platform/IOS: Cisco 2691/12.4(15)T11 Adv IP services
VRFs:
- Customer A: VRF A | IGP: RIP
- Customer B: VRF B | IGP: EIGRP
- Customer C: VRF C | IGP: OSPF 2 Area 0
- ISP: Core IGP: OSPF 1 Area 0 | MP-BGP AS 200
Addressing: See topology. All the routers are configured with a Loopback IP and the format X.X.X.X /32 where X is the router number.
Basic MPLS
I would like to share a basic MPLS configuration example where I will explain how MPLS works and what are the different steps in order to configure it. This example is not related to MPLS layer 3 VPNs, this is just going to be the basic underlying logic of how an MPLS tunnel on its own works so I will neither talk about VRF nor MP-BGP which is the VPNv4 address family in order to exchange the customer routes and the MPLS VPN labels.
Let´s consider the following topology:
PE routers R2 and R4
P router: R3
CE routers R1 and R5
BGP and MPLS completed
It has been a while since I haven´t written in the blog but I have been busy with work and training.
I have now completed my BGP and MPLS exam which will give me a solid understanding for my CCIE training.
In order to pass these 2 exams I have used the student and lab guides from Cisco. I have done all the labs using real device as well as GNS3 (especially for MPLS where I used 13 routers!)
I attach the network diagram I used for MPLS training.